CNC Precision Machining: How Lathes & Turn-Mill Boost Precision
Release time:
2025-04-06
CNC lathe machining, CNC lathe machining and milling machining center are key branches of modern manufacturing industry. Through intelligent control and process innovation, high-precision molding of complex parts is achieved. Among them, CNC lathe machining is the precision benchmark for shaft parts. Its automated tool setting technology, high-speed turning process and multi-axis linkage capability are its technical advantages.
In the field of high-end manufacturing, CNC precision machining has become a core technology for achieving high-precision forming of complex parts through intelligent control and process innovation. As key branches within this domain, CNC lathe machining and turn-mill composite machining centers leverage their unique technical advantages to cover full-scenario machining needs, from shaft-type parts to complex structural components. This article analyzes how these three technologies collectively empower modern manufacturing by examining their technical principles, application scenarios, and process advantages.

CNC Precision Machining: The Foundation of Intelligent Manufacturing
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology drives machine tool movements through program commands, enabling precise control of the machining process. Its core advantages include:
1. Digitalized Machining Process
● Converts part design drawings into CNC codes and uses CAD/CAM software for tool path planning, eliminating manual operation errors and ensuring machining consistency. For example, machining the multi-curved surfaces of automotive engine crankshafts via CNC systems can achieve 0.01mm-level dimensional accuracy control.
2. Multi-Process Integration Capability
● Supports integrated machining of turning, milling, drilling, tapping, and other processes on a single device, reducing positioning errors caused by multiple workpiece clamping—especially suitable for one-time forming of complex geometries.
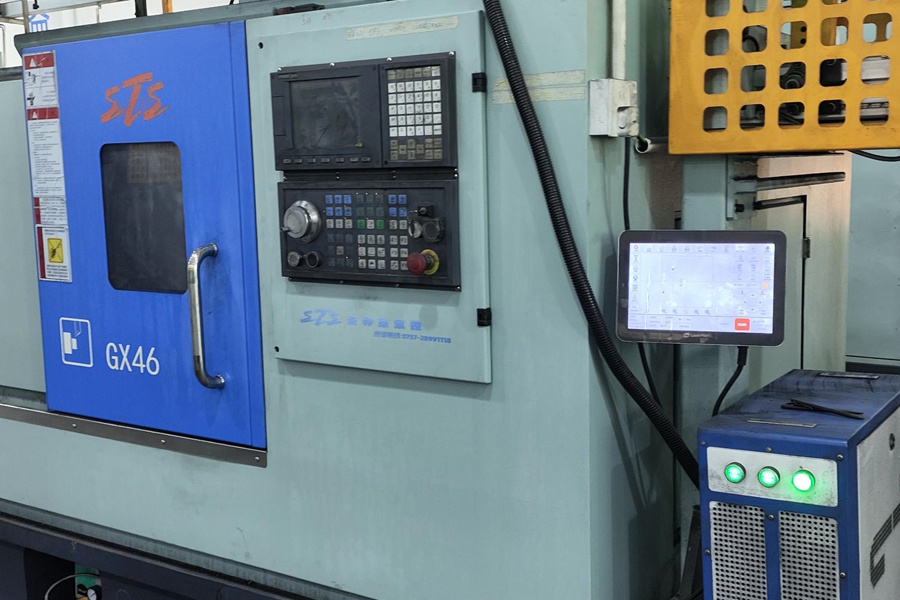

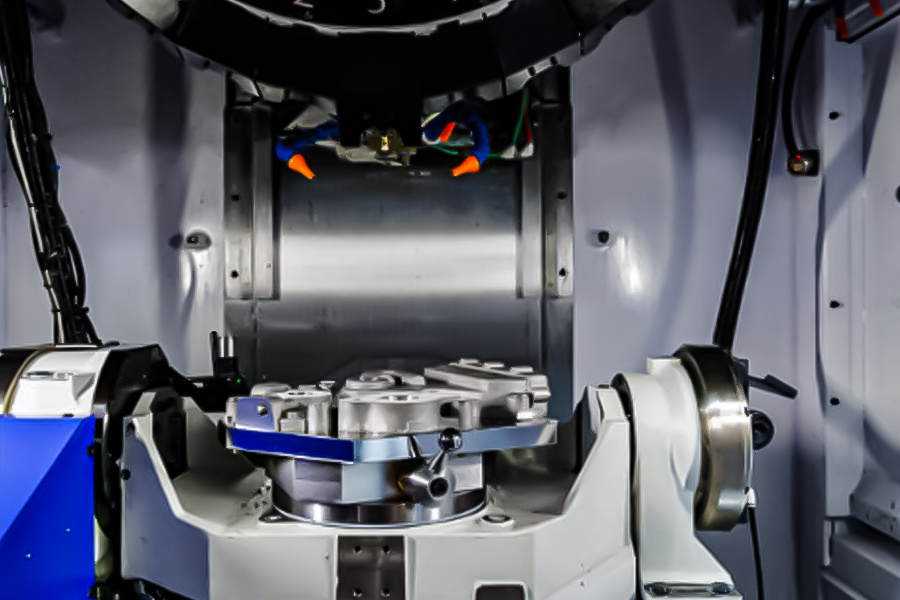
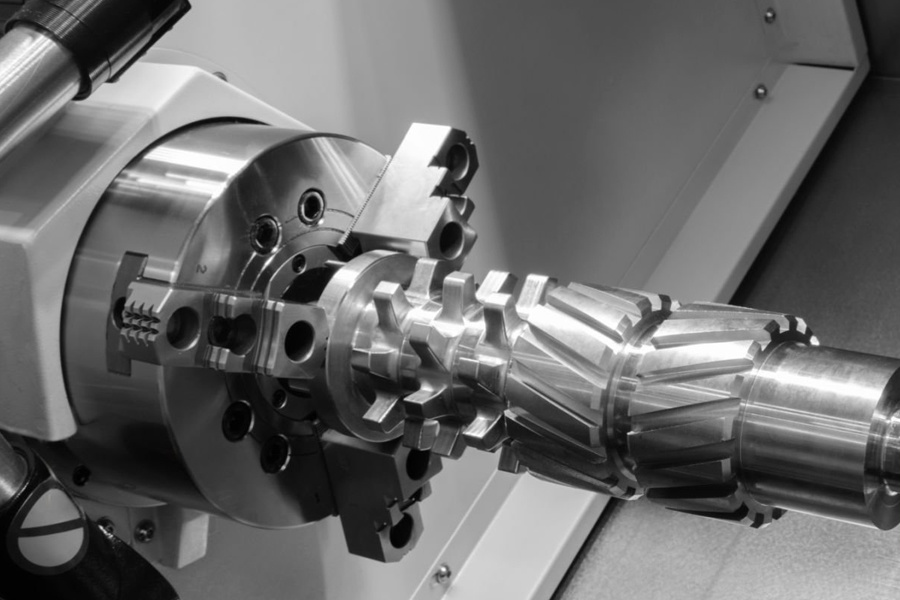
CNC Lathe Machining: The Benchmark for Shaft-Type Part Precision
CNC lathes, characterized by the relative motion between a rotating workpiece and fixed tools, are the preferred solution for machining shaft-type and disk-type parts:
1. Typical Application Scenarios
● Precision shaft machining: Turbine shafts for aerospace and joint shafts for medical devices achieve mirror-like surfaces with surface roughness below Ra0.4 through high-precision spindles (rotational speed stability ≤0.1%);
● Thread machining: CNC systems support complex thread profiles such as multi-start threads and taper threads. Combined with servo turrets for rapid tool changes, efficiency is increased by over 30% compared to traditional lathes.
2. Technical Advantages
● Automatic tool setting technology: Laser tool probes real-time detect tool wear and automatically compensate for offsets, ensuring dimensional consistency in batch processing;
● High-speed turning process: For easy-to-machine materials like aluminum alloys, super-hard tools enable high-speed cutting at linear speeds exceeding 500m/min, achieving surface precision up to IT5 grade.
Turn-Mill Composite Machining Centers: One-Stop Solutions for Complex Parts
Turn-mill composite machining centers integrate the functions of lathes and milling machines, enabling "one-clamping, full-process machining" through multi-axis 联动 (simultaneous motion). They excel in processing polyhedral and curved-surface parts:
1. Technical Breakthroughs
● 5-axis simultaneous machining capability: X/Y/Z linear axes combined with A/C rotational axes allow machining of free-form surfaces on aerospace blades, eliminating tool marks from traditional segmented processing;
● Power tool system: Supports rotating tools such as milling cutters and drills, enabling side milling while the workpiece rotates to achieve high-precision synchronous machining of bearing housing hole systems and planes.
2. Application Fields
● Complex structural components: For example, motor housings in new-energy vehicles undergo one-step machining for internal hole turning, flange surface milling, and heat-dissipating rib processing via turn-mill composites, reducing clamping errors by 60%;
● Miniature precision parts: Multi-segment diameter machining and end-face chamfering of electronic connector pins achieve 0.001mm-level concentricity control through high-precision turntables.
The Manufacturing Logic Behind Precision
The essence of CNC precision machining, CNC lathe machining, and turn-mill composite technology lies in transforming design drawings into reliable industrial entities through "digital control + process innovation." From simple shafts to complex curves, and from single-piece customization to mass production, these three technologies jointly build a full-scenario precision machining system. For high-end manufacturers, choosing processing partners with full technical chain capabilities is not just about obtaining qualified parts but also about solidifying a technical foundation for product performance.
Related Products
CNC machining multi-axis linkage accurately processes tooth profile and journal size
CNC machining technology plays a core role in the machining of precision gears and shaft parts, achieving high-precision micron-level precision, significantly improving the wear resistance and fatigue resistance of parts, and ensuring the stable operation and high quality of the transmission system. In modern industrial manufacturing, its application in automobile manufacturing, precision instruments, industrial equipment and other fields has significantly improved the overall quality.
2025-06-28
Automotive precision parts processing: Use high-precision gears to drive the future of new energy
The development of new energy vehicles has put forward higher requirements for the precision of parts. The breakthrough of micron-level manufacturing technology has laid the foundation for the stable operation of the power system. High-precision gears are innovatively applied in the energy conversion system of new energy vehicles, which reduces friction loss, improves transmission efficiency and prolongs gear life.
2025-06-18
The manufacturing process of precision accessories in modern medical equipment, especially the use of core processing technologies such as CNC turning and laser micro-welding to achieve precise manufacturing in complex medical scenarios. These technologies not only require precise dimensional control, but also must meet biocompatibility and long-term stability.
2025-06-14
Five-axis machining centers have gradually become the core equipment for the manufacture of complex parts due to their multi-dimensional dynamic machining capabilities. Compared with four-axis equipment, five-axis machining centers significantly improve the machining accuracy and surface quality of special-shaped structural parts through multi-angle synchronous cutting, shortening the production cycle.
2025-06-11